The Caspian Sea, with its mesmerizing beauty, is renowned for its remarkable diversity and distinct characteristics. It stands apart from typical saltwater seas due to its varying salinity levels, with the northern regions exhibiting higher salinity than the southern parts. This peculiar feature has given rise to a fascinating array of marine life, including endemic species that have adapted to thrive in this diverse ecosystem. Moreover, the Caspian Sea’s waters hold great importance for the sturgeon, a species that produces the renowned and highly sought-after delicacy known as caviar. However, alongside its ecological wonders, the Caspian Sea faces environmental challenges such as pollution, overfishing, and habitat degradation, necessitating concerted efforts to safeguard its fragile balance and preserve its natural wonders for future generations.
Beyond its natural splendor, the Caspian Sea boasts a rich historical tapestry that intertwines with the destinies of neighboring civilizations. It has been a pivotal trade route, connecting Europe and Asia and facilitating cultural exchange along the ancient Silk Road. The port cities that dot its shores, steeped in history and heritage, bear witness to the vibrant crossroads of diverse civilizations. Additionally, the Caspian Sea’s energy resources, including substantial oil and natural gas reserves, have endowed it with immense geopolitical significance. The exploration and utilization of these resources have shaped diplomatic negotiations and complex power dynamics among the countries bordering the sea. Thus, the Caspian Sea encapsulates natural beauty, historical significance, and the intricate interplay between energy geopolitics and regional cooperation.
Geographical Location and Size of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea, located in the heart of Eurasia, is prominent on the world map as the largest enclosed body of water. Situated between Europe and Asia, this remarkable waterway spans an expansive area, covering approximately 371,000 square kilometers (143,000 square miles). Its strategic location makes it a vital link between regions and influences its diverse geopolitical dynamics.
Geographically, the Caspian Sea is bordered by five countries: Russia to the north, Kazakhstan to the northeast, Turkmenistan to the east, Iran to the south, and Azerbaijan to the west. These nations each have their respective coastlines along the Caspian Sea, with Russia occupying the largest portion. The sea is not connected to any oceans, and its waters are landlocked, giving it the characteristics of a lake rather than a traditional saltwater sea.
The Caspian Sea’s size and depth contribute to its significance globally. Its maximum depth reaches around 1,025 meters (3,363 feet), making it one of the world’s deepest lakes. Moreover, its volume of water is substantial, estimated to be approximately 78,200 cubic kilometers (18,800 cubic miles). The sea’s coastline stretches for about 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles), offering vast potential for various economic activities, including shipping, fishing, and offshore oil and gas exploration.
Understanding the geographical location and immense size of the Caspian Sea provides a foundation for exploring its diverse ecosystems, ecological importance, and historical and geopolitical dynamics that have shaped the region.

Caspian Sea coast in Ramsar, Iran
Salinity and Marine Life of The Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea exhibits a unique balance of brackish water with varying salinity levels throughout its vast expanse. The Caspian Sea stands apart from conventional saltwater oceans as a mixohaline body of water, exhibiting distinct salinity variations across its spectrum. The northern part of the sea, influenced by inflowing rivers and freshwater sources, tends to be less saline. At the same time, the southern portion, closer to the open ocean, has higher salinity levels.
The salinity of the Caspian Sea also fluctuates seasonally due to factors such as rainfall, evaporation, and changes in river water inflow. These variations in salinity impact the sea’s unique ecosystem and the diverse marine life that inhabits its waters.
The Caspian Sea is home to a rich array of flora and fauna adapted to the specific environmental conditions of the region. Various species of fish, including sturgeon, herring, and trout, thrive in its waters, providing a vital source of livelihood and supporting local fishing industries. The sea is particularly renowned for its sturgeon population, known for producing sought-after caviar.
However, over the years, the Caspian Sea has faced environmental challenges that have impacted its marine life. Pollution, habitat degradation, and overfishing have posed significant threats to the delicate balance of this ecosystem. Efforts are being made to address these issues and promote sustainable fishing practices to protect the biodiversity of the Caspian Sea.
Understanding the salinity levels and the unique marine life of the Caspian Sea highlights the importance of conservation and sustainable management to ensure the long-term health and viability of this remarkable body of water and its diverse ecosystem.
The Caspian Sea Environmental Challenges
The Caspian Sea faces several environmental challenges that threaten its delicate ecosystem. One of the main concerns is pollution resulting from industrial activities, oil spills, and agricultural runoff. These pollutants adversely affect the water quality and marine life, leading to habitat degradation and the decline of certain species.
Another significant challenge is the invasive species that have entered the Caspian Sea, disrupting the native biodiversity and ecological balance. Introducing non-native species, such as comb jellyfish and zebra mussels, has had detrimental effects on the native flora and fauna.
Furthermore, the Caspian Sea is experiencing water level fluctuations, which have been attributed to climate change. Rising sea levels, coastal erosion, and increased frequency of extreme weather events threaten coastal communities and their infrastructure.
Efforts are being made to address these challenges and protect the Caspian Sea’s unique environment. International collaborations, conservation initiatives, and implementing sustainable practices are crucial for the long-term preservation of this valuable ecosystem.
Historical Significance of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea holds great historical significance, being an important region that has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations throughout the centuries. It has been a crucial hub for trade, cultural exchange, and geopolitical interactions.
Dating back to ancient times, the Caspian Sea played a vital role in the trading networks of the Silk Road, connecting civilizations in the East and the West. Its strategic location made it a gateway for exchanging goods, ideas, and knowledge between regions.
The Caspian Sea has also been a site of significant historical events and conflicts. Various empires, including the Persian Empire, the Mongols, and the Russian Empire, sought to control and dominate the region due to its economic and political importance. The Caspian Sea has witnessed numerous battles, conquests, and shifts in power throughout history.
In addition to its historical importance, the Caspian Sea is associated with a rich cultural heritage. The diverse ethnic groups inhabiting its surrounding regions have contributed to the cultural tapestry of the area, resulting in a unique blend of traditions, languages, and customs.
Today, the Caspian Sea is strategically important due to its vast energy resources, particularly oil and gas. The exploration and extraction of these resources have shaped the modern geopolitical dynamics of the region.
Beneath the Caspian Sea’s surface lie extensive oil and natural gas reserves, making it a critical player in global energy markets. Exploiting and exploiting these resources have created complex geopolitical dynamics and disputes among neighboring countries. Resolving these issues necessitates diplomatic negotiations and cooperative efforts to ensure the sustainable utilization of this invaluable natural asset.
What countries are exploiting the Caspian Sea?
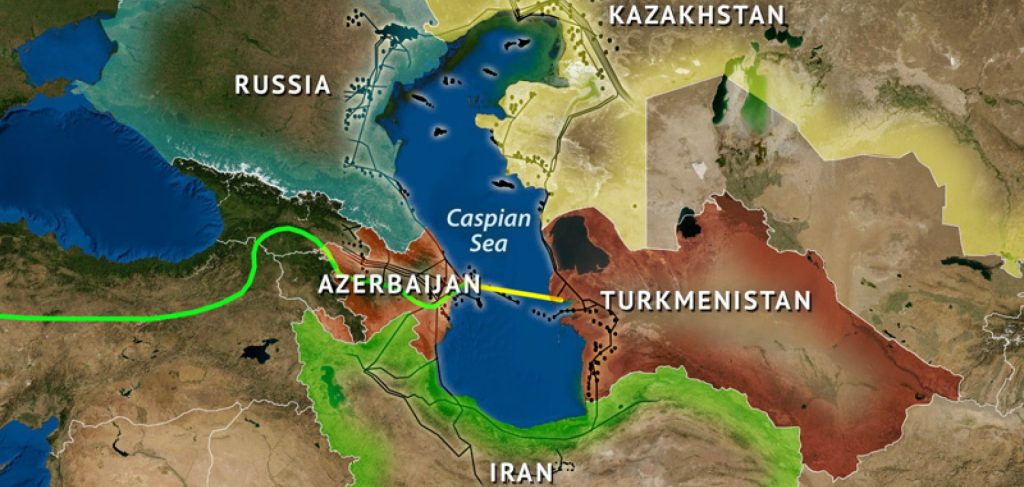
Which countries are exploiting the Caspian Sea?
Several countries surrounding its shores are exploiting the Caspian Sea, each with its interests and activities. The countries involved in the exploitation of the Caspian Sea include:
- Russia: As the largest country bordering the Caspian Sea, Russia plays a significant role in its exploitation. It has extensive oil and gas exploration and production operations in the Russian sea sector. Russia has the largest share of the Caspian Sea, accounting for approximately 21% of its total area.
- Kazakhstan: Like Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan has significant oil and gas reserves in its section of the Caspian Sea. The country has been actively engaged in exploration and production activities, aiming to harness its energy resources for economic development. Kazakhstan holds around 15% of the Caspian Sea’s area, making it the second-largest stakeholder in the region.
- Azerbaijan: With its substantial offshore oil and gas reserves, Azerbaijan has been actively developing energy resources in the Caspian Sea. It has established major oil and gas fields, contributing to economic growth and energy exports. Azerbaijan holds around 11% of the Caspian Sea’s area, securing a notable portion of the sea for its maritime activities.
- Turkmenistan is another country with notable hydrocarbon reserves in the Caspian Sea. It has been involved in offshore drilling operations to tap into its oil and gas potential. Turkmenistan possesses approximately 13% of the Caspian Sea’s area, giving it a significant portion of the sea.
- Iran: Iran also shares a coastline with the Caspian Sea and has its energy exploration efforts in the region. It has explored and exploited oil and gas reserves in its sea sector. Iran has a share of approximately 11% of the Caspian Sea, making it one of the key countries with access to its waters.
These countries have been engaged in bilateral and multilateral agreements to address issues related to resource exploration, territorial disputes, and environmental concerns in the Caspian Sea. Exploiting the sea’s resources has significant economic implications for these countries, contributing to their energy sectors and overall development.
Conclusion
The Caspian Sea is a remarkable testament to nature’s power and our world’s interconnectedness. Its unique characteristics, diverse ecosystems, and historical significance make it an awe-inspiring destination for adventure seekers and those interested in comprehending the intricate fabric of our planet. By appreciating and safeguarding this majestic body of water, we can ensure its preservation for future generations.




No comment